July
Things to do in the garden:
Fill gaps with pretty little winter-hardy plants like sea thrift (Armeria maritima), candytuft (Iberis sempervirens) and wild carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus).
Cold winters result in rodents building nests under the roof, in garden sheds, cupboards, under the fridge and behind bookcases. There are products available to dispatch them promptly, that are friendly to both humans and other animals.
Create new paths. This is the best time to access the structure of your garden in terms of pathways and accesses. Widen pathways that are being taken back by the encroaching garden by adding more pavers.
Divide thick clumps of rhubarb and re-plant and plant asparagus crowns.
Divide overgrown bromeliads and replant them. Try to find interesting ways to display these interesting plants all over your garden.
Winter care for compost heaps includes turning them over and adding commercial compost activators to break down the plant material more quickly. They are available from hardware stores and nurseries.
Conifers are growing actively now and can be pruned lightly to shape them neatly. Never cut into old wood, but rather shave off healthy foliage and growing tips with sheep shears or a hedge clipper – this will result in fresh, dense growth.
Clean up bamboos, nandinas and flaxes by cutting out old stems and tidying up at their bases.
Check winter bedding plants and remove any damaged leaves, as well as those affected with mildew or black spots.
Keep on planting winter- and springflowering annuals like pansies, violas, cinerarias and calendula.
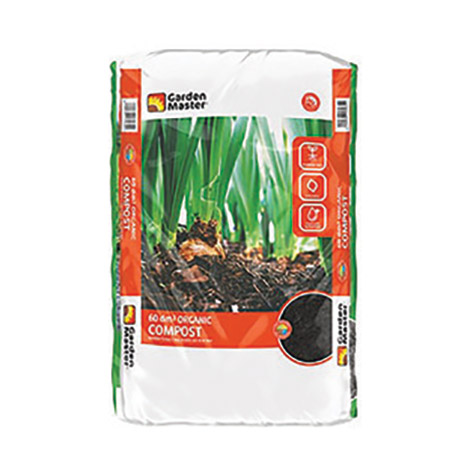

Garden Master Organic Compost improves water retention, rejuvenates soil and increases beneficial microbes. Available in 30 dm and 60 dm bags.
Credits
Referenced from Garden Master: Autumn / Winter Garden Calendar